Hernia Surgery
30+ Years of surgical experience
What is a Hernia?
A hernia (external) is a protrusion of an internal body structure, or part of an organ through a weakness in the protective outer muscle-fascia covering like the protrusion of the inner tube through a weak area in the outer pneumatic tire. Hernia (internal) can also occur inside the body between spaces within like Hiatus Hernia. Hernia can cause pain, swelling or malfunction (e.g. vomiting) of a stuck protruding organ (e.g. bowels) by compressing it.
What causes hernia?
Prolonged rise in pressure due to persistent cough (e.g. smoker’s cough), breathing difficulty (COPD), constipation, straining to pass urine, obesity, pregnancy, fluid collection (ascites) pushes internal structures through any weakness in the covering structures. Such weak spots may be a birth defect, or due to stretching as in pregnancy, obesity, or following injury/ surgery, or aging.
Where does Hernia occur?
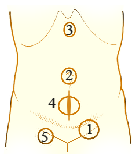
| 1. Inguinal Hernia | This is the commonest site. It is in the groin fold and depending on the site of weakness called Indirect/ Direct/ Pantaloon (Direct+Indirect). These are more common among women. | |
| 2. Umbilical Hernia | Occurs at the navel and depending on the site of weakness called Umbilical or Para umbilical. These are often seen with obesity, pregnancy or ascites. | |
| 3. Epigastric Hernia | Seen in the breastbone and the navel. | |
| 4. Incisional Hernia | Occurs at the scar of an abdomen surgery /injury. | |
| 5. Femoral Hernia | It is uncommon. It is seen below the groin fold and is more common among women. | |
Obturator hernia, Perineal hernia, Lumbar hernia, Interstitial hernia , Spigelian hernia and many more rare hernias occur at unusual sites.
What are the possible complications of Hernia?
Irreducible Hernia (also known as incarcerated): the hernial contents cannot be returned to their normal site with simple manipulation
Obstruction: compression of the herniated bowel can obstruct passage of food leading to stomach bloating, cramps, and later on vomiting, and inability to pass flatus and stools.
Strangulation: Crushing of the hernial contents may compromise blood supply and can cause death of the herniated structures (necrosis, gangrene), which may prove fatal.
These signs mandate urgent surgery.
How is a Hernia treated?
As the hernia is caused by a weak spot , it needs surgery to correct it and cannot be treated by medicine. Traditional stitched repair (Herniorrhaphy) is out of flavor now because it is often under tension and the stitches can tear out producing an even bigger hernia. A ‘Tension free Hernia’ repair using a patch of synthetic material is done to treat the hernia by either open surgery or laparoscopic surgery. Open surgery can be done under Local anesthesia, as a day care procedure, and even in those unfit for General anesthesia.
